Depth of Field (DoF) Techniques for AI Image Generation
Depth of Field (DoF) is a key idea in photography. It's about how much of a photo looks sharp. Knowing DoF helps make better AI-made pictures. Things that change DoF are the camera's opening, lens length, and how far away stuff is. By manipulating DoF, we can emphasize a subject by blurring the background, or ensure everything in the scene remains in focus for a more detailed view.

Several factors influence Depth of Field:
- Aperture (Camera Opening): The size of the camera's aperture is a primary determinant of DoF. A wider aperture (lower f-number) results in a shallower depth of field, blurring the background and making the subject stand out. Conversely, a smaller aperture (higher f-number) increases the depth of field, keeping more of the scene in focus.
- Focal Length of the Lens: Longer lenses (higher focal length) typically produce a shallower depth of field compared to shorter lenses. This characteristic makes telephoto lenses popular for portraits, where a blurred background is often desirable.
- Subject Distance: The closer the subject is to the camera, the shallower the depth of field. This principle is particularly useful in macro photography, where focusing close to the subject dramatically blurs the background.
- Sensor Size: Cameras with larger sensors also affect the depth of field. Larger sensors tend to provide a shallower depth of field at the same aperture setting compared to cameras with smaller sensors.
In the context of AI-generated imagery, understanding and simulating these aspects of DoF allows for the creation of images that feel more realistic and visually appealing. AI can use models of these parameters to adjust the focus precisely, enhancing the artistic or communicative intentions of the image.
AI algorithms, prompted with depth of field keywords, can manipulate visual focus to guide viewer attention, convey mood, and express artistic vision.
Deep Focus: Making Everything Sharp
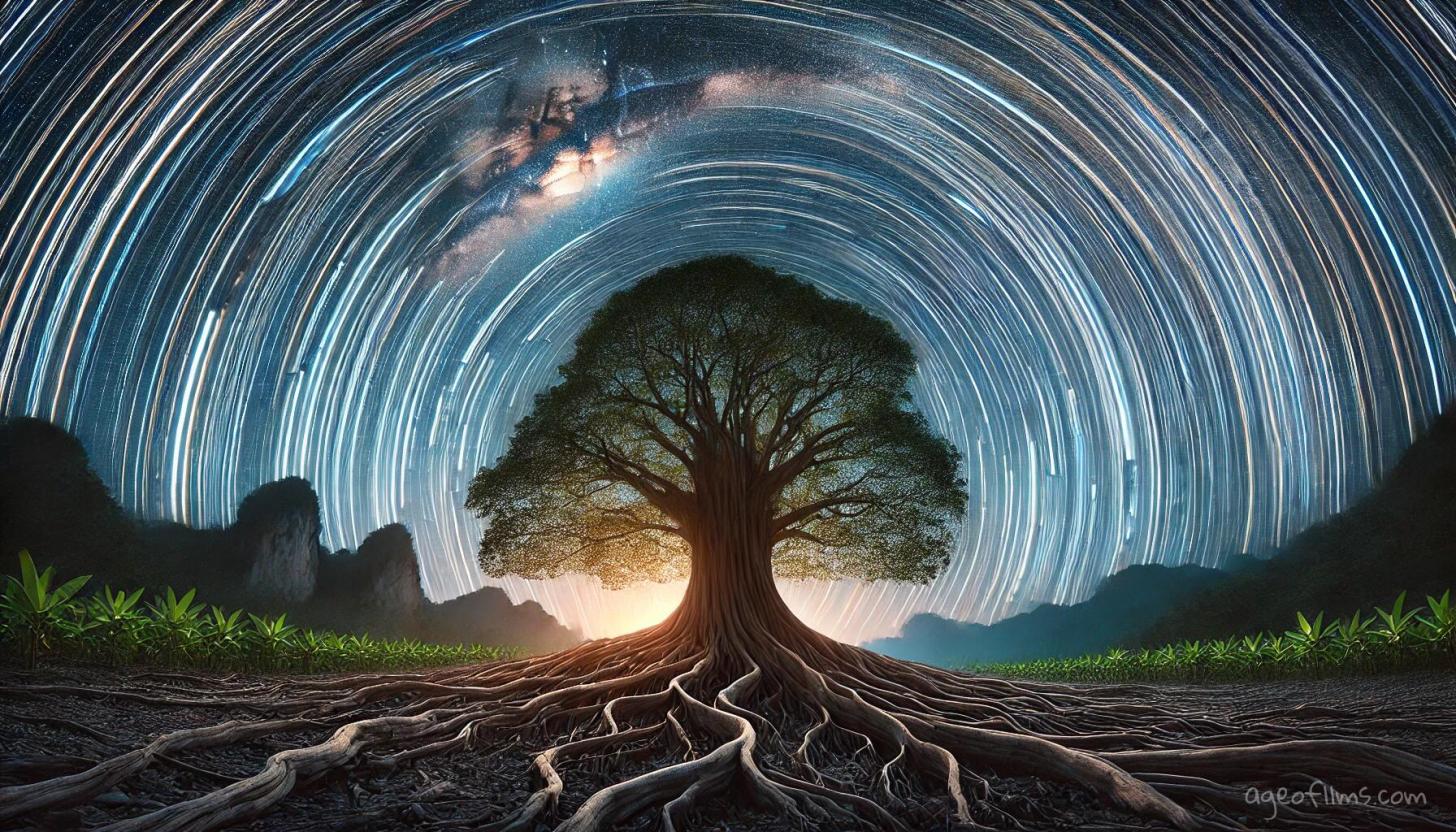

Deep focus makes most of the picture look clear, from front to back. You do this by using a small camera opening and a wide lens.
It's great for:
- Big outdoor scenes
- Taking pictures of buildings
- Street photos
To make AI draw this, you could prompt:
Generate an image of a vast landscape with sharp details from foreground to background, emulating deep focus.
Hyperfocal Distance: Getting the Most Sharpness
Hyperfocal distance is a trick to make as much as possible look sharp. It's about focusing at just the right spot to make everything from pretty close to really far away look clear.
It's useful for:
- Big outdoor scenes
- Street photos
- Pictures of buildings
Prompt AI:
Make a street photo with clear details from close things to far-away stuff, using hyperfocal distance.
Difference Between Hyperfocal Distance and Deep Focus
Think of hyperfocal distance like a magic spot. When you focus your camera on this spot, you get the most stuff in focus possible. It's like a sweet spot that makes everything from about halfway to that point all the way to infinity look sharp.
Deep focus is when you make almost everything in your picture look sharp, from stuff that's close to you all the way to things far away. It's like making sure every part of your photo is clear, no matter where it is.
The big difference is how you get there:
- With hyperfocal distance, you're finding one perfect spot to focus on.
- With deep focus, you're using camera settings (like a small opening) to make everything look clear.
- Both make lots of your picture sharp, but hyperfocal is a specific technique, while deep focus is more of a general look you're going for.
Here's ChatGPT's input on where the difference lies:
| Aspect | Hyperfocal Distance | Deep Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Technique | Focus is set at the hyperfocal distance to maximize depth of field. The foreground and background are both in acceptable focus, with slight falloff in sharpness towards extreme distances. | Focus is set to ensure everything from the foreground to the background is sharply in focus. Achieved by using a small aperture (higher f-stop) and sometimes additional lighting. |
| Effect | This technique ensures that everything from half of the hyperfocal distance to infinity is in acceptable focus, making it ideal for landscapes where both the foreground and background need to be sharp. | The entire scene, from front to back, appears sharp and clear. This technique emphasizes all elements in the frame, creating a sense of space and continuity. |
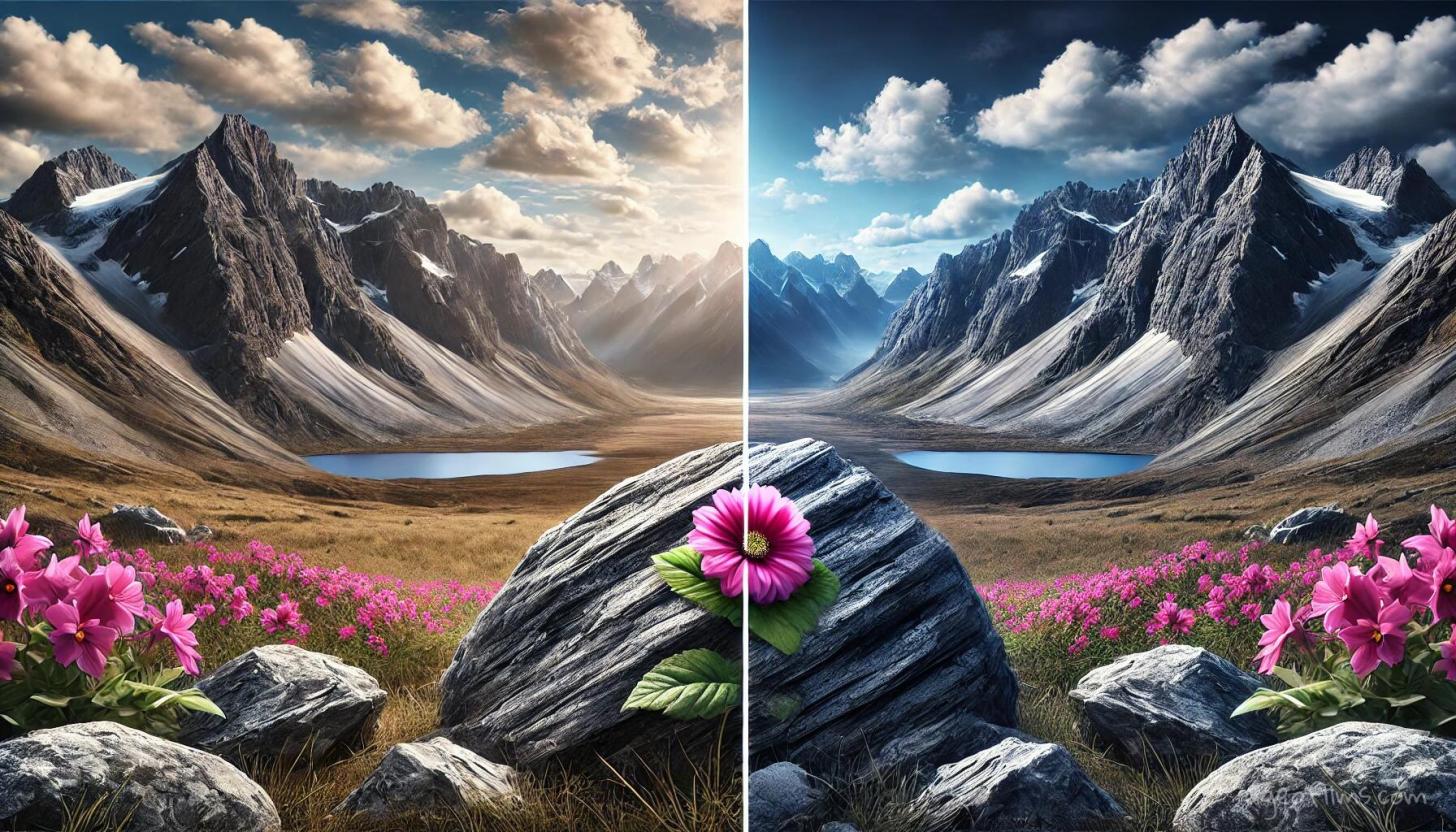

A landscape photograph with a foreground element (like a rock or flower) close to the camera and a distant mountain range in the background.Focus Stacking: Putting Sharp Parts Together
Focus stacking means taking lots of pictures with different focus points and mixing them. This makes one super-clear picture. It's really good for close-up shots.
It works well for:
- Very close-up photos
- Taking pictures of products
- Outdoor scenes with lots of detail
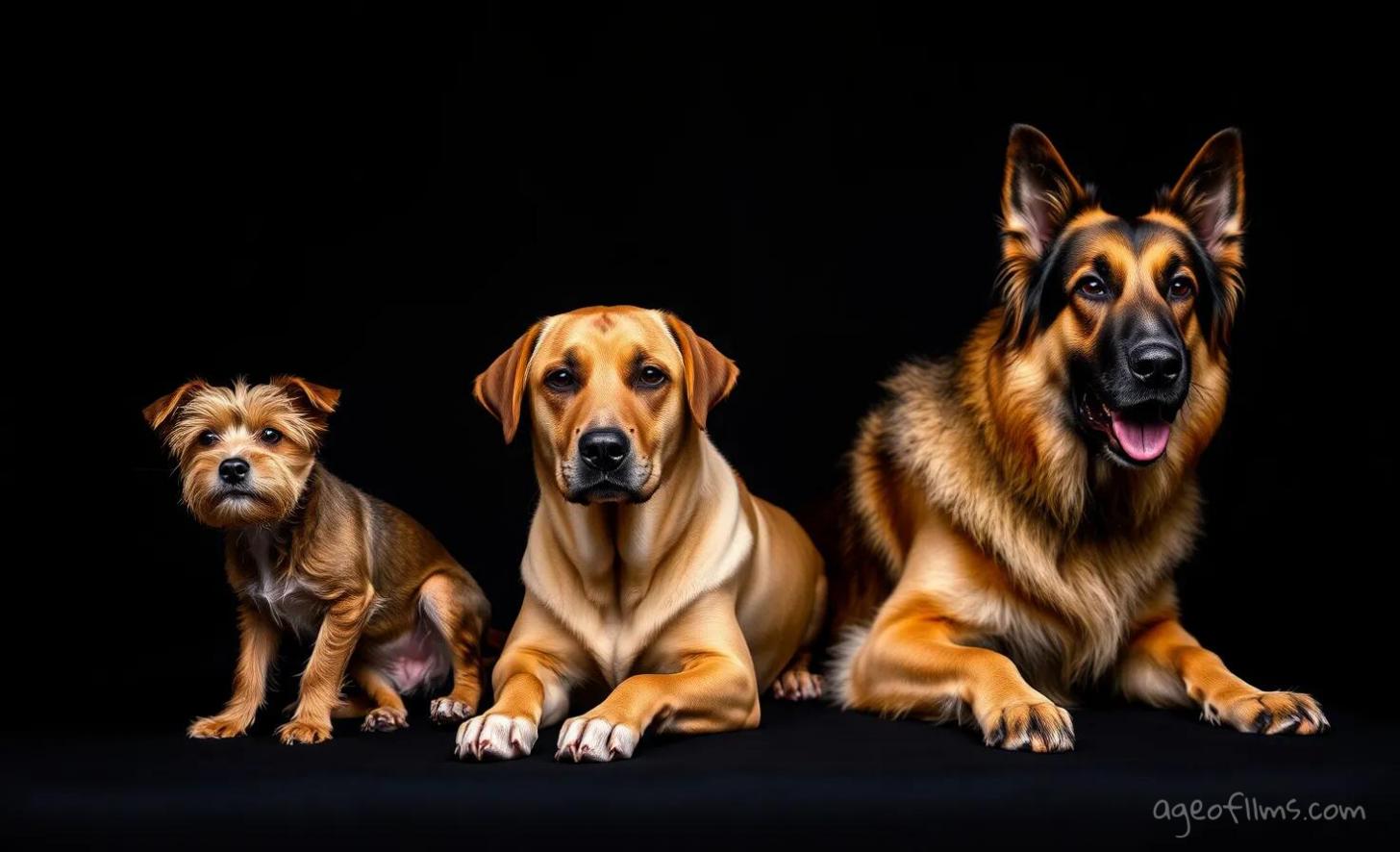

Prompt example:
Three dogs of varying sizes positioned at different distances from the camera against a dark, uniform studio background. Each dog should be in perfect focus, from the closest to the furthest, showcasing their unique fur textures and expressions vividly. The first dog, a small terrier, is closest to the camera; the second, a medium-sized labrador, is in the middle; and the third, a large shepherd, is furthest away. Use focus stacking to ensure that each dog's features are equally sharp and detailed, with no part out of focus due to depth of field limitations. The lighting should highlight the dogs' features against the dark background, emphasizing the effectiveness of focus stacking in creating depth and detail across different planes.
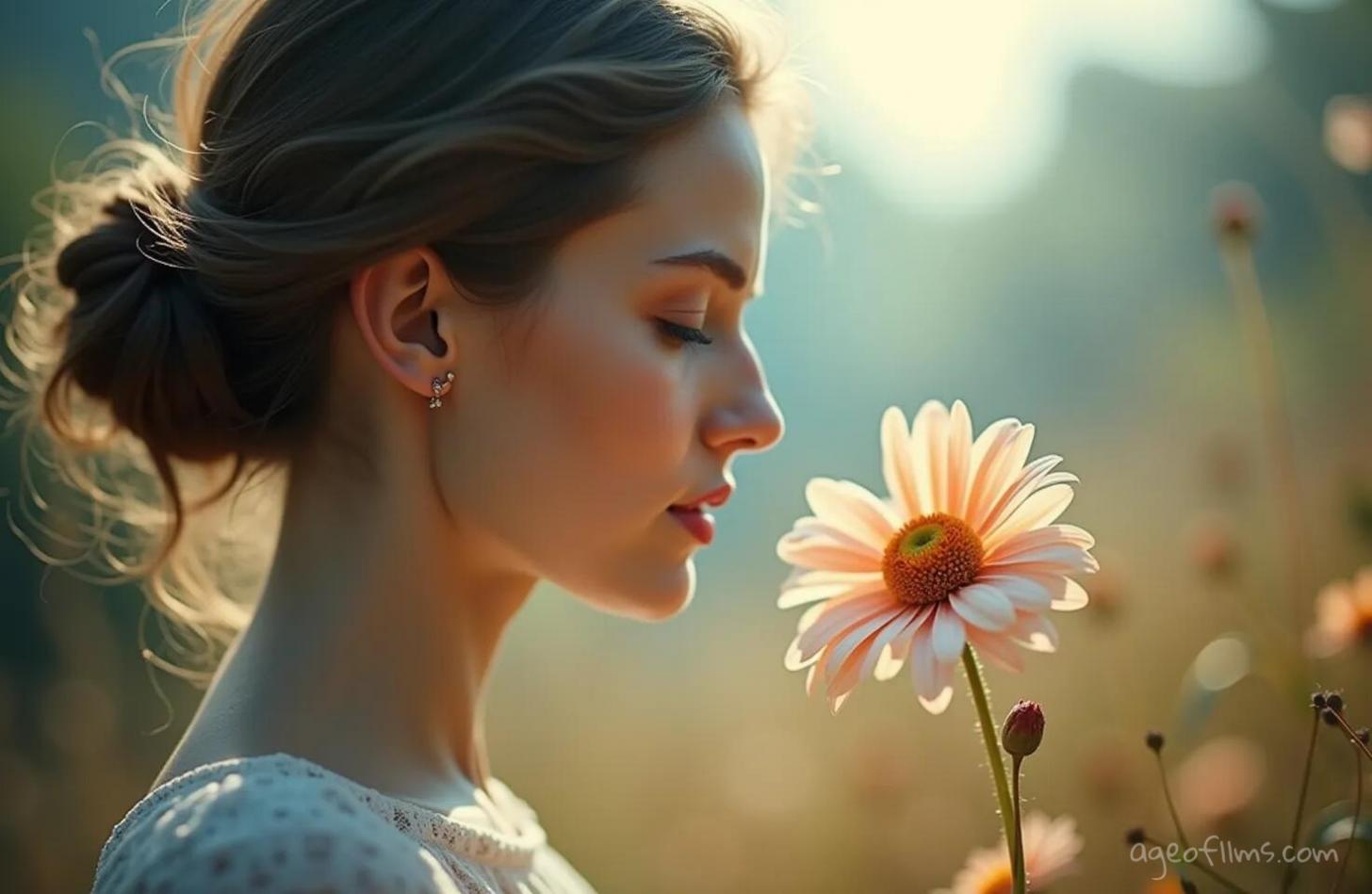
Selective Focus: Making One Thing Stand Out
Selective focus makes the main thing in the picture clear while blurring the rest. You do this with a big camera opening and a long lens.
It's good for:
- People pictures
- Animal photos
- Still life shots
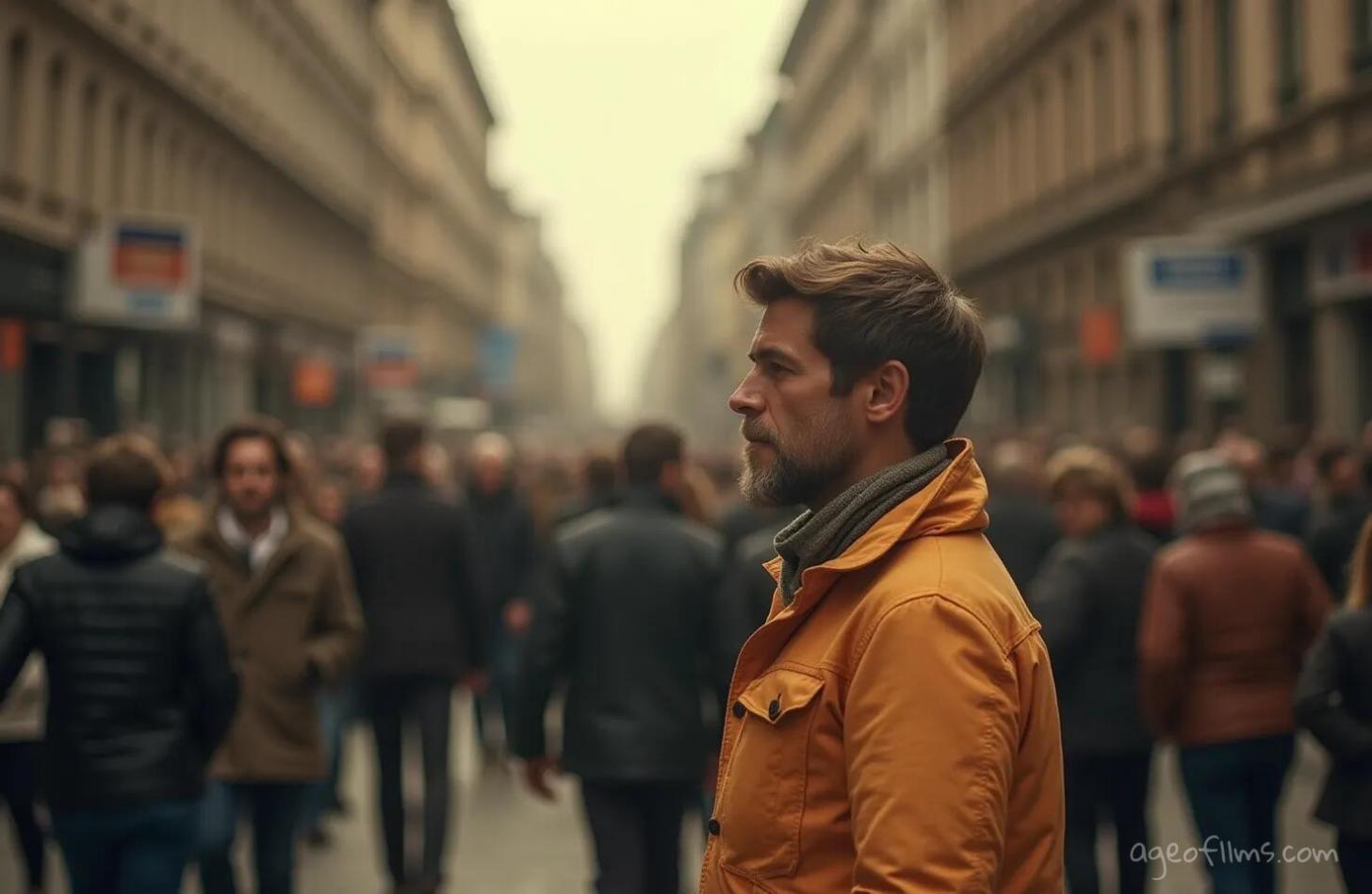

Prompt for selective focus image:
A city street where a crowd of people, all in muted tones, walks away from the camera, symbolizing conformity and the monotonous flow of daily life. In stark contrast, one man, vividly depicted in sepia tones, is in sharp focus. He stands facing the camera, his expression resolute as he prepares to turn and walk towards it. This man is dressed distinctly from the rest, perhaps in a bright color that makes him visually pop against the sepia and muted backdrop. His action and appearance challenge the norm and signify a philosophical stand on individuality and the choice to go one's own way. The overall mood is thoughtful and introspective, with the selective focus drawing the viewer's eye directly to him, making a powerful statement about identity and choice in a conforming world.
Another example with an animal:
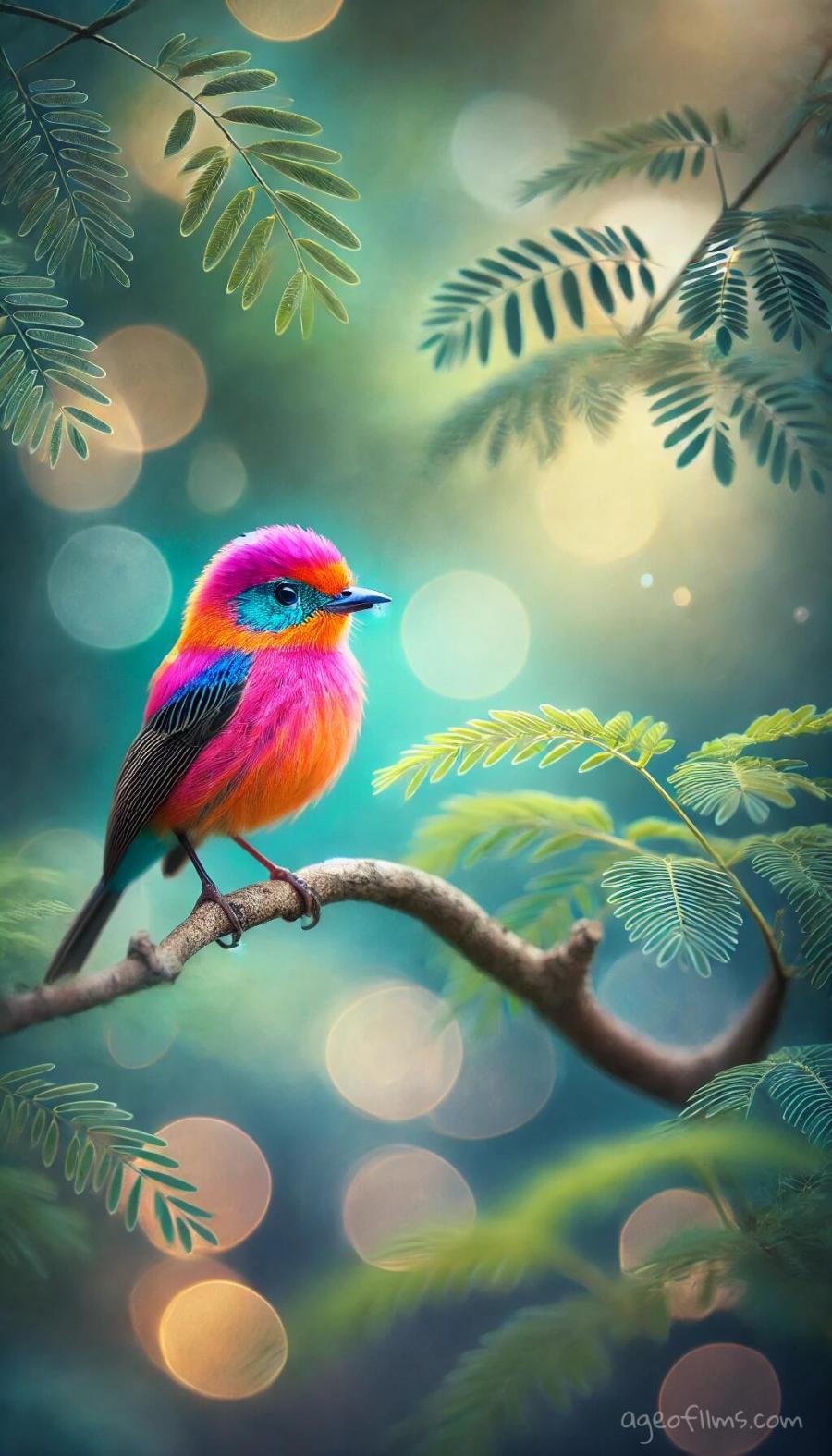

A vibrant bird perched on a delicate branch. The bird should be in razor-sharp focus, showcasing the intricate details of its feathers, the glint in its eyes, and the texture of its beak. Surrounding it, the rest of the scene—including the branch, leaves, and background—should gently blur into soft, out-of-focus shapes, highlighting the bird as the centerpiece. The background hints at a lush, natural environment but remains subtly out of focus to emphasize the bird’s presence. The image should convey a sense of tranquility and elegance, with the bird standing out boldly against the dreamy, blurred backdrop.
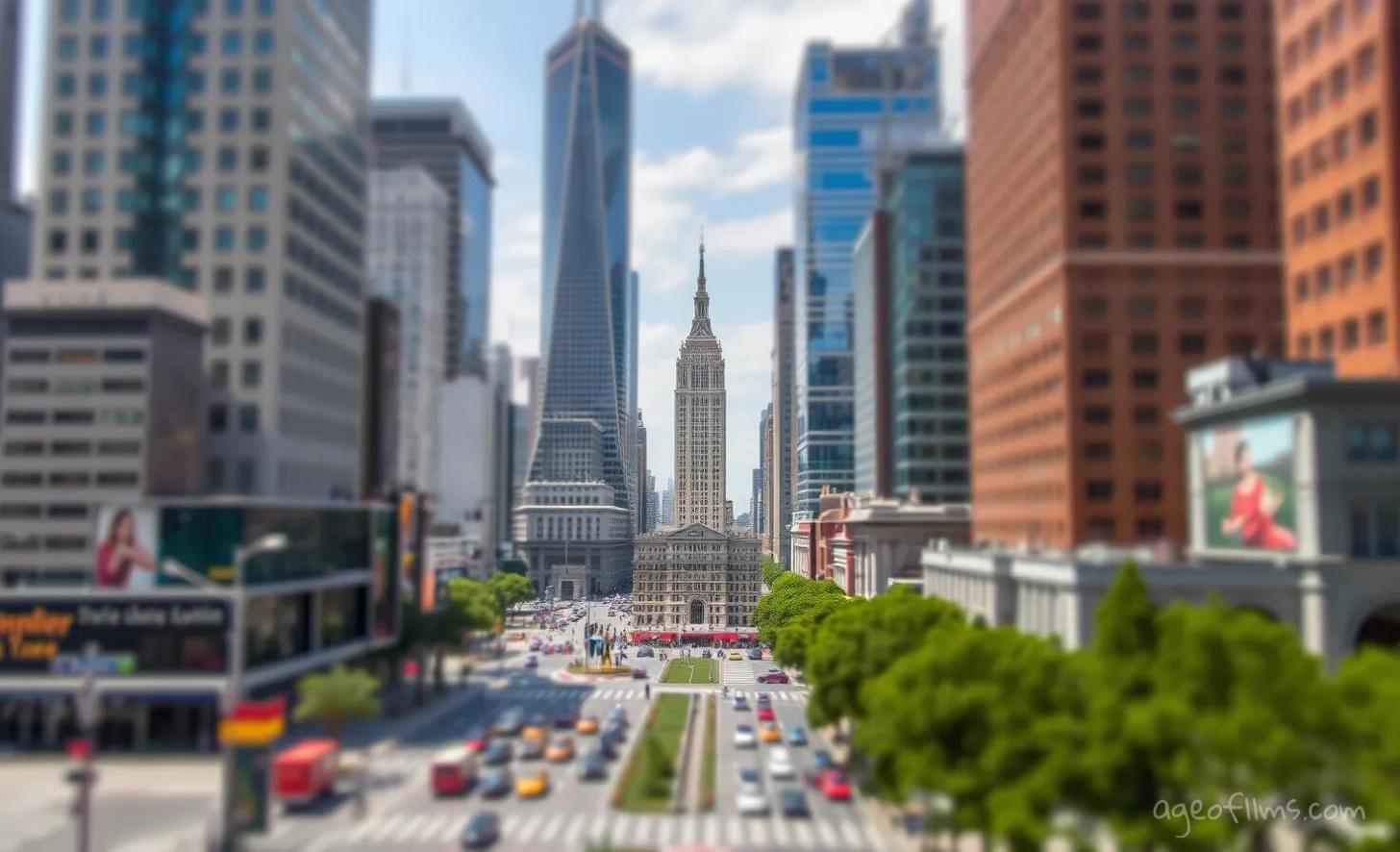
Tilt-Shift: Playing with Focus in Fun Ways
Tilt-shift uses special lenses to change where things are in focus. It can make big things look tiny.
It works for:
- City views
- Outdoor scenes
- Building photos
Example tilt-shift prompt:
An enchanting tilt-shift image of a bustling cityscape during daylight. The scene should be crafted so that skyscrapers, busy streets, and moving vehicles look like intricate miniatures. Focus should be sharply centered on a specific part of the city, such as a notable building or a central street, with the surrounding areas gradually blurring out. This focus manipulation should evoke a playful, toy-like essence of the city, making viewers marvel at the delightful transformation of everyday scenes into the realm of the whimsical and tiny.

Bokeh: Making Pretty Blurs
Bokeh, a beloved photographic effect, celebrates the aesthetic quality of blur. Bokeh is about how nice the blurry parts look. It often shows up as soft, round shapes.
Originating from the Japanese word for "blur" or "haze," bokeh transforms the out-of-focus areas of a photograph into soft, round orbs of light that enhance the visual appeal of the composition. This effect is achieved by using a fast lens at its widest aperture, which allows for a shallow depth of field. The result? A stunning contrast where the main subject is crisply detailed against a canvas of glowing, ethereal spots.
It's great in:
- People pictures
- Nature shots
- Still life photos
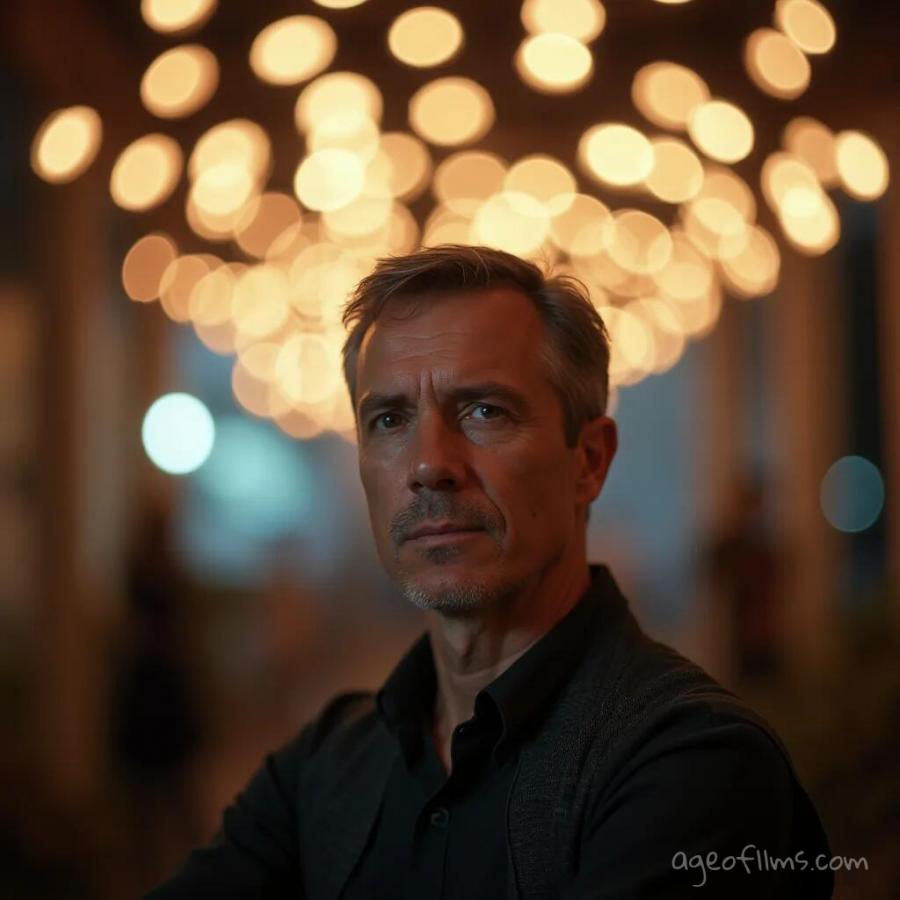
Bokeh prompt example:
The image features a man in his 40ies in sharp focus, positioned prominently in the foreground. He appears contemplative, capturing the viewer's attention with his expressive gaze. Behind him, the backdrop is illuminated with large, round, and soft bokeh lights that shimmer in varying sizes and intensities. These bokeh lights create a magical and dreamy atmosphere, enhancing the depth and mood of the scene. The overall effect is serene and somewhat surreal, emphasizing the contrast between the sharply focused man and the softly blurred lights in the background.

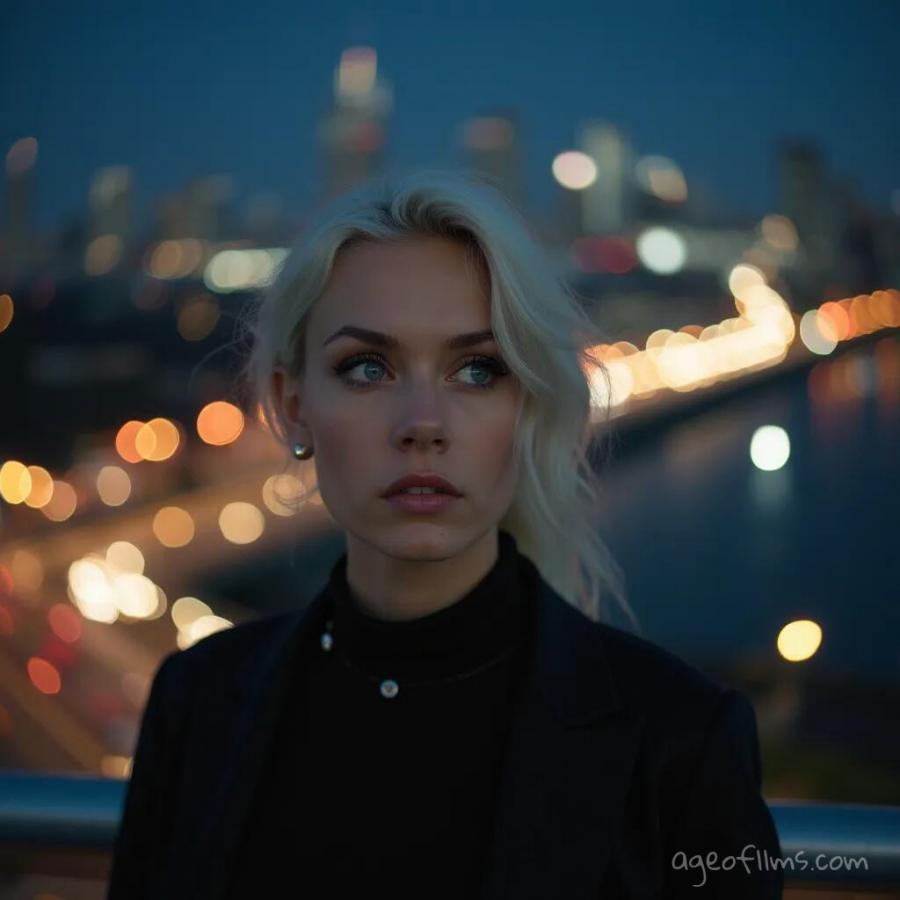
Another example for bokeh:
The image features a platinum blonde white-skinned 30-year-old woman with dark eyebrows, dark blue eyes and prominent dark eye-lashes, gazing expressively and intensely somewhere into the distance. Woman is in focus, positioned prominently in the foreground, possibly standing on the bridge overlooking a busy night city. Behind her, the backdrop is illuminated with night city bokeh lights that shimmer in varying sizes and intensities. These bokeh lights create a philosophical and somewhat mysterious atmosphere, enhancing the depth and mood of the scene.

Mixing Techniques for AI Pictures
You can mix these ideas to make cooler AI pictures. Here are some examples:
"Make a nature scene with a clear, close-up flower in front, blurry pretty background, and a sharp far-away view."
"Create a city that looks like a toy model, with one clear person in front and a blurry background."
In conclusion, knowing these photo tricks helps you prompt AI how to make pictures that look just how you want.
Last modified 07 September 2024 at 09:39
Published: Aug 27, 2024 at 1:40 AM